Ever wondered why some gym-goers never seem to suffer from injuries, while others are constantly sidelined? It all comes down to knowledge and practices that make a significant difference in injury risk.
This comprehensive guide on how to manage a gym will explore the common types of gym injuries, their causes, signs, treatment options, and most importantly, prevention strategies. By understanding these factors, gym owners can create an environment that emphasizes not just fitness, but also the well-being and safety of their members.
Stick around, and discover how to keep gym members fit, healthy, and away from preventable injuries.
Table of Contents
1. Common Types of Gym Injuries
By understanding the range of injuries that can occur, gym owners will be better equipped to implement effective preventive measures and respond appropriately if an injury does happen. Let’s discuss some of the most common ones:
Strains and Sprains
These prevalent injuries typically occur when gym-goers push themselves beyond their physical threshold. A strain happens when a muscle or a tendon – the fibrous tissues connecting muscles to bones – is overstretched or torn. Sprains, on the other hand, affect the ligaments, the fibrous bands joining bones together. They occur when a ligament is stretched beyond its limit or torn, often as a result of a sharp twist or fall.

Fractures
According to Cleveland Clinic, a bone fracture happens when something hits your bone with enough force not only to damage it, but to break it in at least one place. These can result from high-impact activities, unexpected falls, or accidents involving gym equipment. Fractures can range from hairline cracks to complete breaks, and can sometimes necessitate surgery for proper healing.
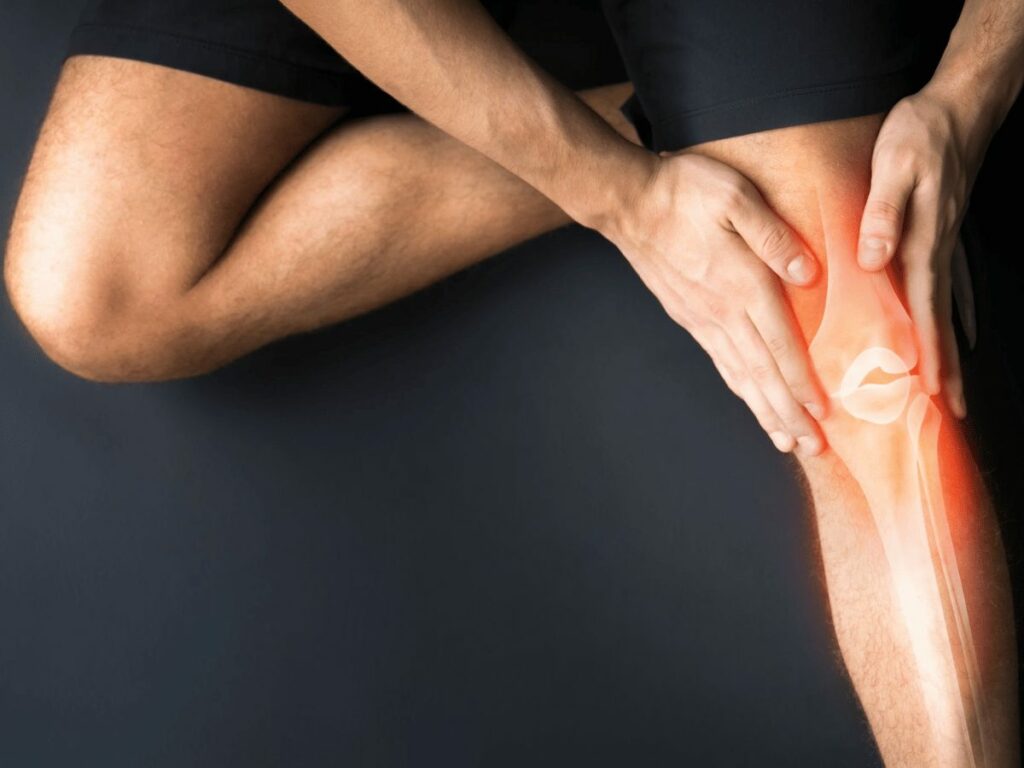
Tendinitis
This condition stems from the inflammation or irritation of a tendon, causing pain and discomfort around a joint. Tendinitis is often a consequence of repetitive, minor impact on the affected area, or from a sudden, more serious injury. Regular gym activities like running, jumping, or lifting weights can lead to tendinitis if not performed with proper form and adequate rest periods.

Hernias
A hernia occurs when an organ pushes through an opening in the muscle or tissue that holds it in place. In the context of a gym, hernias commonly occur due to improper lifting techniques and excessive strain, especially during weightlifting. As such, it is imperative to teach and emphasize correct lifting techniques to minimize the risk of hernias.
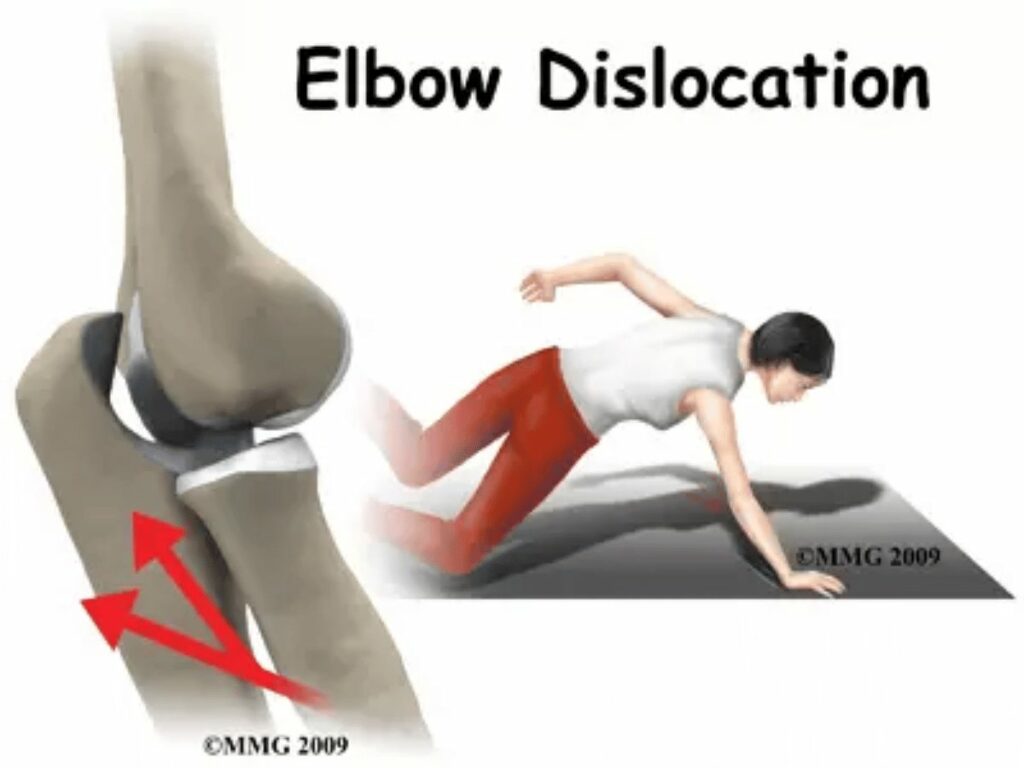
Dislocations
When a joint experiences an impact or fall that forces the bones out of their normal position, a dislocation occurs. Common sites for dislocations include the shoulder, elbow, and fingers. These injuries can cause intense pain and visible deformity, and need immediate medical attention.
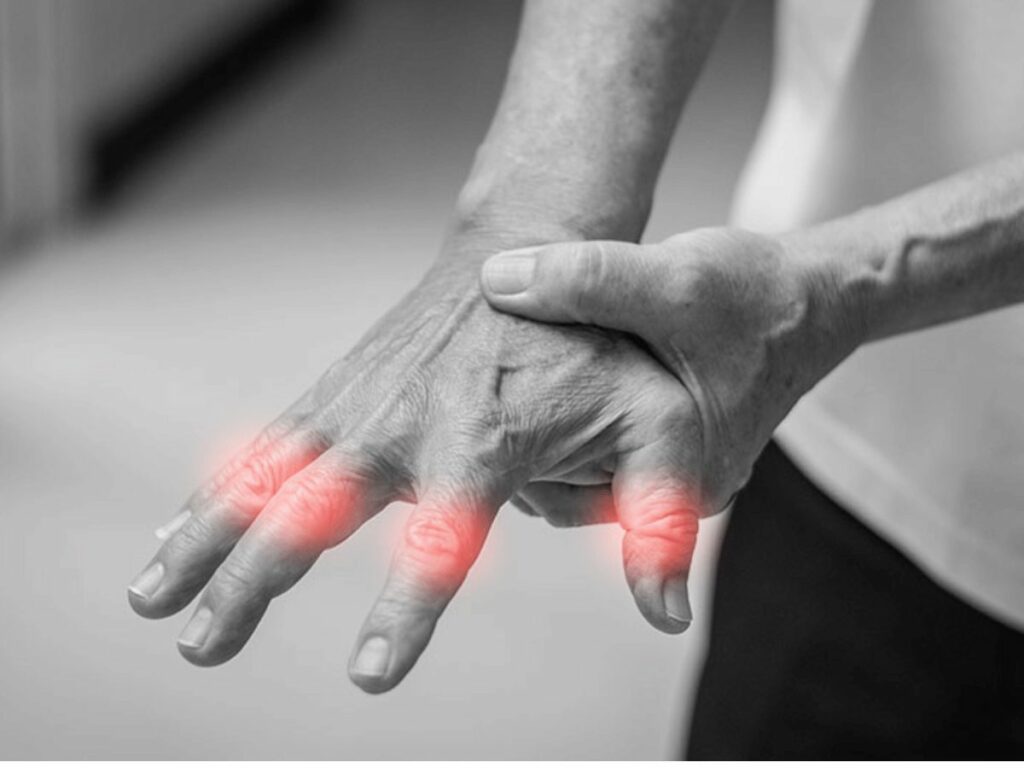
Overuse Injuries
As the name implies, overuse injuries occur from the repetitive use of a certain muscle group without allowing sufficient recovery time. Stress fractures and tendinitis often fall into this category. Overuse injuries are a testament to the adage “too much of a good thing can be bad.”
2. Causes of Gym Injuries
Gym injuries often stem from a variety of factors. Identifying these causes is the first step in mitigating the risk of injuries in a gym environment. Here’s an in-depth look:
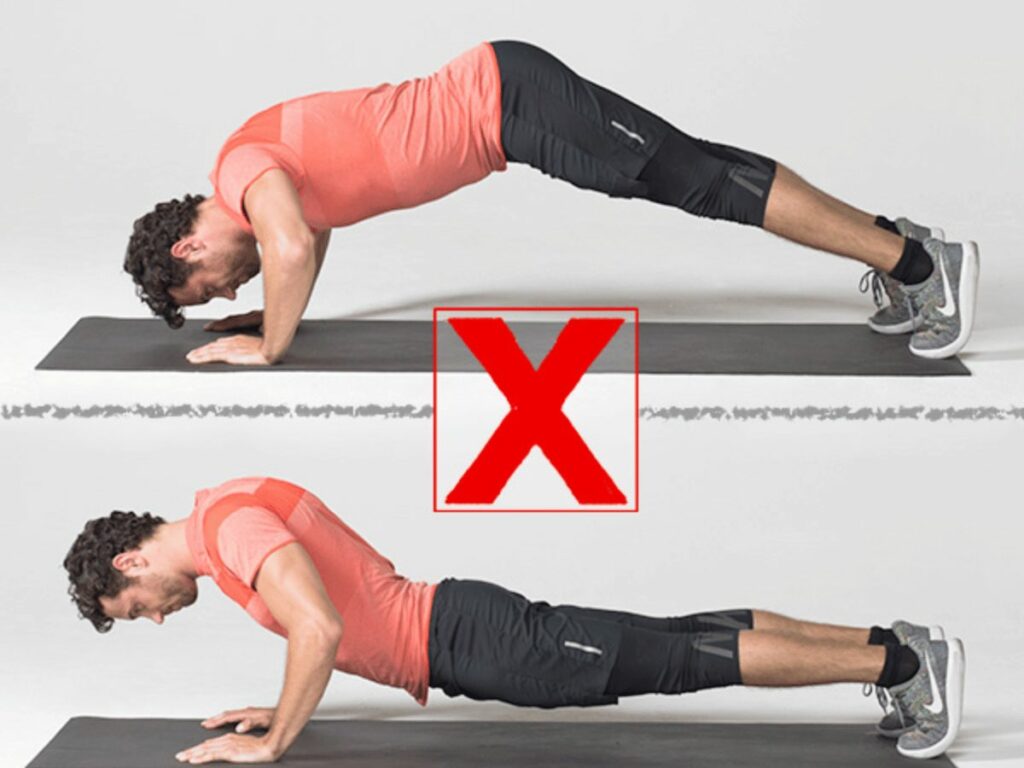
Incorrect Form or Technique
Improper form or technique stands as one of the most significant causes of gym-related injuries. It’s not uncommon to see enthusiastic members adopting incorrect forms when lifting heavy weights or performing complex exercises. This erroneous approach can put undue stress on muscles and joints, precipitating a host of injuries like strains, sprains, and even fractures.

Overexertion and Overtraining
Overexertion and overtraining manifest when an individual consistently pushes beyond their physical limits without allowing their body adequate recovery time. It’s a common misstep among gym-goers, often leading to overuse injuries, including tendinitis and stress fractures. Encouraging members to listen to their bodies and understand the difference between a challenging workout and one that is excessively straining is crucial.

Neglecting Warm-ups and Cool-downs
Many gym members underestimate the importance of proper warm-ups and cool-downs. A comprehensive warm-up prepares the body for the workout ahead, raising body temperature, improving flexibility, and enhancing performance. Meanwhile, cool-downs gradually bring the heart rate down and return the body to its resting state, aiding in recovery and preventing stiffness.
Not Properly Using Gym Equipment
Gym equipment misuse is a prominent cause of injuries in the gym setting. Equipment like treadmills, elliptical trainers, free weights, and resistance machines, if not used correctly, can lead to a variety of injuries, from minor sprains to severe fractures. At Yanre Fitness, our focus is not just on creating high-quality equipment, but also on ensuring that the design is intuitive and user-friendly, reducing the risk of injury due to misuse.
Lack of Personal Training or Guidance
Working out without proper guidance, especially for novice gym-goers, can be a recipe for injuries. Personal trainers play a pivotal role in instructing members on correct exercise form, the safe use of gym equipment, and the importance of balanced, varied workouts. A lack of such guidance can leave members prone to injury.
Ignoring Body Signals
Many gym members have a ‘push-through-the-pain’ mentality, ignoring the body’s signals that something is not right. Yanre Fitness believes in the importance of educating gym owners and members about the significance of recognizing and respecting their body’s signals. Creating a safer gym environment doesn’t stop at providing top-quality equipment—it includes fostering an informed and health-conscious community.
3. Signs and Symptoms of Gym Injuries
Identifying gym injuries at the earliest stages can prevent them from escalating into more serious conditions. Here are some telltale signs and symptoms that shouldn’t be ignored:
Pain and Discomfort
Pain or discomfort stands out as one of the most immediate and noticeable signs of a gym injury. This sensation can persist throughout the day or may only surface during certain activities or movements. Pain is the body’s mechanism of signalling a potential problem, and hence, should never be overlooked. In my opinion, any persistent pain that does not dissipate with rest and time warrants further attention.
Swelling or Redness
According NIH, when a wound swells up, turns red and hurts, it may be a sign of inflammation. The swelling is the result of an accumulation of fluid in the tissues following an injury, whereas redness typically arises from inflammation. These signs are particularly common with injuries such as sprains, strains, fractures, or tendinitis, where the body’s inflammatory response is activated to protect the area and initiate healing.
Decreased Range of Motion
A gym injury can often lead to a noticeable decrease in the range of motion, making it challenging to move the affected joint or muscle group as freely as usual. This symptom is prevalent in cases of tendinitis, severe sprains or strains, and certain types of fractures. If an individual finds it difficult to perform usual movements or if movements cause discomfort, it could indicate an underlying injury.
Bruising or Discoloration
Bruising, characterized by a change in skin color to blue or black, is another sign of an injury. It occurs when small blood vessels under the skin tear or rupture, often due to a sprain, strain, or impact from a fall or collision with gym equipment. A bruise may initially appear reddish and then become bluish-black or purple within a few hours or days.
Visible Deformity
In some instances, injuries such as dislocations or fractures may result in a visible deformity. For instance, the affected area may appear out of alignment or have an unusual bump or break in the bone’s normal line. Believe me, this is a clear indication of a serious injury that requires immediate medical attention.
Weakness or Instability
If a gym-goer feels weak or unstable while standing or moving, it could be a sign of an underlying injury. Weakness may manifest as a sudden inability to use the affected muscle group effectively, while instability may cause a feeling of the joint “giving way.” These symptoms are commonly associated with sprains, strains, and certain types of fractures.
Prolonged Stiffness
Prolonged stiffness after a workout, beyond the usual muscle soreness, might be a sign of an overuse injury. If a gym member experiences difficulty moving a joint due to stiffness, especially in the mornings or after periods of inactivity, it might indicate an injury like tendinitis or a stress fracture.
4. Treatment of Gym Injuries
When gym injuries occur, appropriate management is essential to ensure quick and effective recovery. Here’s how to deal with them:
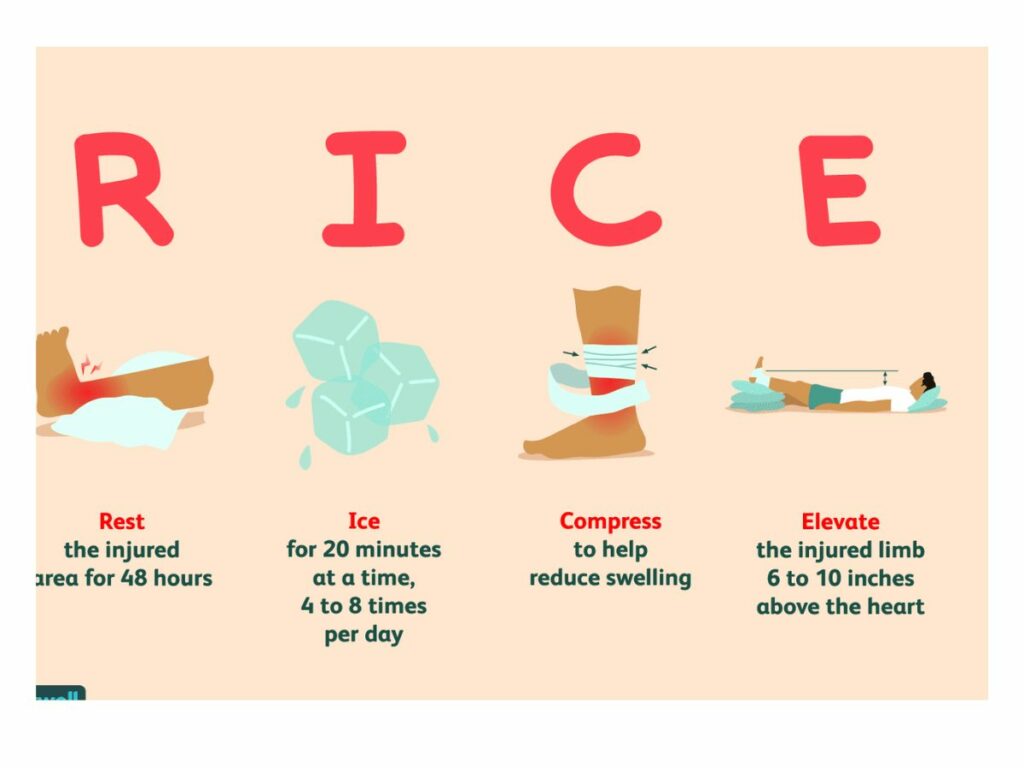
Initial Steps: Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation (RICE)
The RICE method is a simple, self-care technique that helps reduce swelling, ease pain, and speed up healing. Rest involves avoiding activities that cause pain. Ice is used to reduce swelling and numb the affected area. Compression, such as bandages, helps to minimize swelling, while Elevation aids in reducing swelling by controlling blood flow.
Seeking Medical Attention
Severe injuries, such as fractures, dislocations, or severe sprains, require immediate medical attention. Based from experienc, health professionals can provide appropriate treatment options, which might include pain management, immobilization of the injury, or in some cases, surgery.
Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation
Physical therapy and rehabilitation play a crucial role in the recovery process, especially for severe injuries or post-surgery. Skilled physical therapists can guide gym members through specific exercises designed to restore strength, flexibility, and mobility to the injured area. This can speed up recovery, prevent reinjury, and ensure a safe return to regular gym activities.
This table provides an overview of the key aspects involved in physical therapy and rehabilitation for gym treatment injuries, including goals, assessment, treatment modalities, and collaborative care.
| Topic | Description |
| Goal | Restore strength, flexibility, and mobility to the injured area, speed up recovery, prevent reinjury, and ensure a safe return to regular gym activities. |
| Assessment | Conduct a thorough assessment of the injury, including range of motion, muscle strength, pain levels, and functional limitations. |
| Treatment Plan | Develop a customized treatment plan tailored to the individual’s injury and specific goals. This may include a combination of therapeutic exercises, manual therapy, modalities, and functional training. |
| Therapeutic Exercises | Prescribe exercises targeting the injured area to improve strength, flexibility, and stability. Exercises may include stretching, strengthening, balance training, and functional movements. |
| Manual Therapy | Utilize hands-on techniques, such as joint mobilization, soft tissue mobilization, and massage, to reduce pain, improve range of motion, and promote tissue healing. |
| Modalities | Implement various modalities, such as heat therapy, cold therapy, electrical stimulation, ultrasound, or laser therapy, to alleviate pain, reduce inflammation, and promote tissue healing. |
| Education | Provide education on proper body mechanics, injury prevention strategies, and self-management techniques to empower individuals to take an active role in their recovery and prevent future injuries. |
| Progress Tracking | Regularly evaluate and track progress through objective measures, such as strength and range of motion assessments, to modify the treatment plan and ensure continuous improvement. |
| Home Exercise Program | Design and prescribe a home exercise program to encourage consistent participation and facilitate progress between therapy sessions. |
| Collaborative Care | Coordinate with other healthcare professionals, such as orthopedic surgeons or sports medicine specialists, to ensure comprehensive care and a seamless transition from rehabilitation to regular gym activities. |
Pain Management
Depending on the severity of the injury, pain management may involve over-the-counter pain relievers or prescription medications. It’s crucial to use these under the guidance of a healthcare provider to manage side effects and avoid potential complications. In some instances, alternative pain management techniques such as massage, acupuncture, or heat and cold therapy might also be beneficial.
Surgical Intervention
In cases of severe fractures, dislocations, or certain types of tendon injuries, surgical intervention may be necessary. This is typically considered as a last resort when other treatment options have failed or when the injury is so severe that surgery is the only viable solution. Post-surgery, a period of physical therapy is usually recommended to restore functionality to the affected area.
Psychological Support
It’s important to acknowledge that dealing with a gym injury can also have a psychological impact. Feelings of frustration, depression, or anxiety are not uncommon. Providing psychological support through counselling or support groups can be a vital part of the recovery process, helping gym members cope with their situation and encouraging a positive mindset towards recovery.
5. Prevention of Gym Injuries
While it’s impossible to eliminate all risk of injury, certain strategies can significantly reduce the likelihood. Here are some of the most effective measures:
Proper Warm-ups and Cool-downs
Integrating comprehensive warm-up and cool-down routines before and after workouts respectively can go a long way in preventing injuries. Warm-ups prepare the body for the upcoming physical exertion, while cool-downs help bring the body back to its resting state, enhancing recovery and reducing post-workout stiffness.
Correct Exercise Technique and Form
Ensuring correct exercise technique and form is crucial in preventing gym injuries. This includes proper alignment, using the right muscle groups, and controlling movements. I highly suggest having trained professionals on hand to guide and correct gym-goers can make a significant difference in injury prevention.
Adequate Rest and Recovery
The body needs time to repair and strengthen itself after a workout. Introducing sufficient rest periods between workouts, and ensuring a good night’s sleep, allows for optimal recovery and minimises the risk of overuse injuries.
Gradual Progression in Exercise Intensity
Encouraging gym members to gradually increase the intensity of their workouts can help prevent injuries. This allows the body time to adapt to new stresses, reducing the risk of strains, sprains, and other injuries. Additionally, this approach nurtures a culture of patience and respect for one’s own physical limitations, fostering a long-term, sustainable commitment to fitness.
Regular Equipment Maintenance and Safety Checks
Regular maintenance and safety checks of gym equipment can ensure it’s in good working condition, reducing the risk of injury from malfunctions or failures. This also includes ensuring the equipment is used correctly by members, offering guidance as necessary.
Balanced and Varied Workouts
Promoting balanced and varied workouts can prevent overuse injuries and provide all-round fitness benefits. This includes a mix of cardio, strength training, flexibility exercises, and balance training. It helps ensure different muscle groups and joints get worked, reducing the risk of overloading any one part of the body.
6. Conclusion
Gym injuries can be prevented, treated, and recovered from by implementing proper training techniques, warm-up exercises, and post-workout care. Opening a gym and educating your clients on injury prevention and management is crucial for maintaining a safe workout environment and ensuring their long-term success.
To further enhance your gym’s safety standards, invest in Yanre Fitness equipment. Our durable, high-quality products are designed with user safety in mind. Contact us today for more product details, catalogues, price lists, or any additional support for creating an injury-free workout space for your clients.
Related articles:








